不同的散列方式。
取余法、平方取中法、乘法杂凑法、线性探测法 linear probing、二次探测法 quadratic probing、双散列函数 double hashing、分离链接法 separate chainging。
# Lecture05 - 散列函数
# 简介
散列表 (Hash function/name-address function)
Address = hash (key),将搜索的复杂度降到常数复杂度 O (C)

如何解决冲突?
α=n / b
n 是元素个数,b 是桶的数目
# 散列函数
# 取余法
大小通常取最大质数,避免造成散列中存在始终未用到的部分。
# 平方取中法
先进行原来的数据进行平方,然后取八进制,再选取中间的合适部分。
# 乘法杂凑函数
M 是表长?
用一个无理数乘 key 值然后丢掉整数得到小数部分。
# 针对字符串 - 1
to add up the ASCII (or Unicode) value of the characters in the string. 把字符串中的每一个字符的 ASCII 值或者 Unicode 值相加
public static int hash( String Key, int tableSize ) { | |
int hashVal = 0; | |
for( int i = 0; i < Key.length( ); i++ ) | |
hashVal += Key.charAt( i ); | |
return hashVal % tableSize; | |
} |
如果字符串长度很短,那么会集中在前面的散列表
# 针对字符串 - 2
前面乘一个乘数,把数据打散
# 如何解决散列表冲突问题
碰撞的两个 (或多个) 关键码称为同义词,即 H (k1)=H (k2),k1 不等于 k2
# linear Probing (线性探测法)
If hash(key)= d and the bucket is already occupied then we will examine successive buckets d+1, d+2,……m-1, 0, 1, 2, ……d-1, in the array
如果 key 的哈希值是 d,并且 d 对应的位置已经被占据,然后我们会按照线性顺序向后成环形查找
散列表已经满了之后,算法复杂度比较高,需要遍历整个散列表
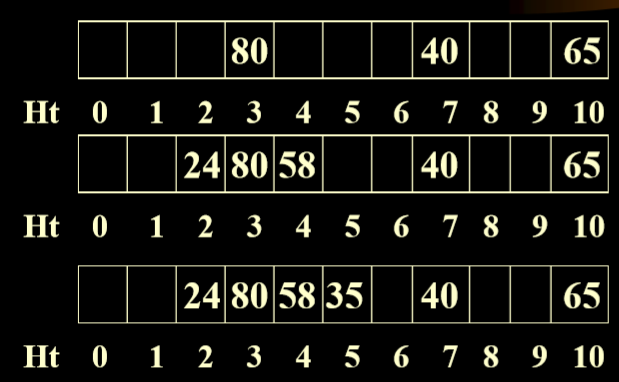
# 例一
放入 58 的时候和 80 冲突,因此放到下一个 4
同理,放入 35 的时候冲突
计算例一中的平均成功访问次数
58 查 2 次,35 查 4 次
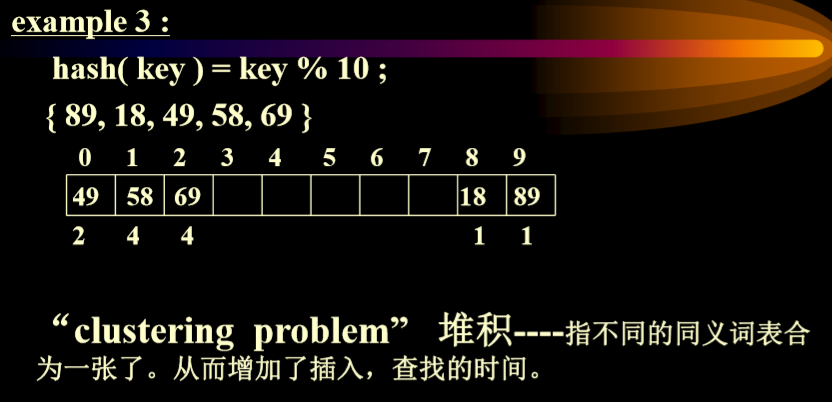
# 例二
线性表示法的弊端 —— 堆积问题
如果一个地方发生了冲突,那么周围的复杂度会迅速升高
查询 35 从位置 2 开始查询,不是的话查询下一个。如果 58 被删除,35 在寻访位置 4 的时候是空的,停止查询。
不能直接删除线性表中的数据,应该是进行标记,标志该元素已经删除。
# 线性探测法的 c++ 实现
//hashtable 的构造方法 | |
template<class E,class K>//E 和 K 需要被实例化后,这个类才能被调用。 | |
HashTable<E,K>::HashTable(int divisor){ | |
D = divisor; | |
ht = new E[D]; | |
empty= new bool[D]; | |
for(int i=0;i<D;i++) | |
empty[i] = true; | |
} | |
template<class E,class K> | |
int HashTable<E,K>::hSearch(const K&k)const { | |
int i= % D;//home bucket | |
int j= i ; //start at home bucket | |
do { | |
if(empty[j] || ht[j]==k) return j;//fit | |
j= (j+1) % D; //next bucket | |
} while(j != i); //returned to home? 是否循环完成一遍 | |
return j; //table full; | |
} | |
// 参数进行引用 K&k | |
template<class E,class K> | |
bool HashTable<E,K>::Search(const K&k,E&e)const{ | |
//put element that matches k in e. | |
//return false if no match. | |
int b= hSearch(k); | |
if(empty[b]||Hash(ht[b])!=k)return false; | |
e=ht[b]; | |
return true; | |
} | |
template<class E,class K> | |
HashTable<E,K>& HashTable<E,K>::Insert(const E& e) { | |
K k=Hash(e);//extract key | |
int b=hSearch(k); | |
if(empty[b]){ | |
empty[b]=false; | |
ht[b]=e; | |
return *this; | |
} | |
throw NoMem(); //table full | |
} |
# 二次探测法 (Quadratic probing)
quadratic 平方

注意,平方如果冲突之后,是在原来的位置 - 1, -4, -9 进行循环的
# 实现方法
public interface Hashable { | |
int hash(int tableSize); | |
} | |
class HashEntry { | |
Hashable element; | |
boolean isActive; | |
public HashEntry(Hashable e){this(e, true); | |
} | |
public HashEntry(Hashable e, boolean i) { | |
this.element = e; | |
this.isActive = i; | |
} | |
} | |
public class QuadraticProbingHashTable { | |
public QuadraticProbingHashable() | |
public QuadraticProbingHashable(int size) | |
public void makeEmpty( ) | |
public Hashable find(Hashable x) | |
public void insert(Hashable x) | |
public void remove(Hashable x) | |
public static int hash(String key, int tableSize) | |
private static final int DEFAULT_TABLE_SIZE = 11; | |
protected HashEntry [ ] array; private int currentSize; | |
private void allocateArray(int arraySize ) | |
private boolean isActive( int currentPos ) | |
private int findPos( Hashable x ) | |
private void rehash( )// 需要扩大 hash 表大小的时候,再哈希 | |
private static int nextPrime( int n ) | |
private static boolean isPrime( int n ) | |
} |
# 双散列哈希 (Double Hashing)
If hash1(k)= d and the bucket is already occupied then we will counting hash2(k) = c, examine successive buckets d+c, d+2c, d+3c……,in the array
如果 k 的第一哈希值为 d,而这个对应的格子已经被占用则我们继续计算 k 的第二哈希值,然后检查 d+c…
第一个散列函数发生冲突,那么使用第二个散列函数来放置,如果再次冲突则进行相应探测。
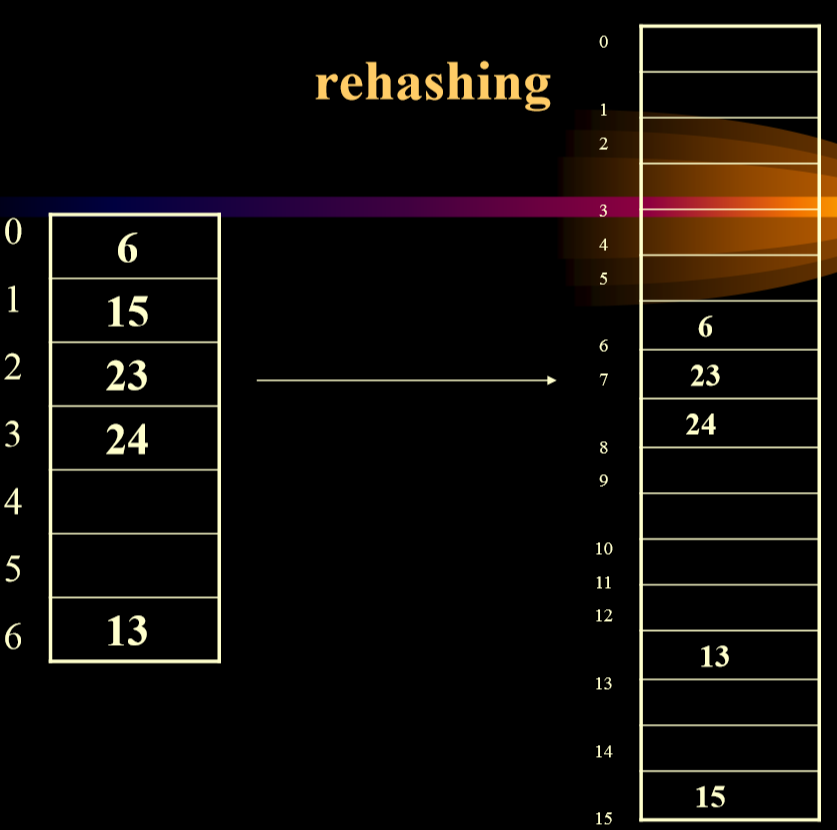
再散列 (进行扩容)
尽量保证表项数 > 表的 70%,也就是意味着如果不满足,就需要进行再散列。
# 再散列的实现
private void rehash(){ | |
HashEntry [] oldArray = array ; | |
allocateArray(nextPrime(2*oldArray.length)); | |
currentSize = 0; | |
for( int i = 0;i < oldArray.length;i++ ) | |
if(oldArray[i] != null && oldArray[i].isActive) | |
insert(oldArray[i].Element); | |
} |
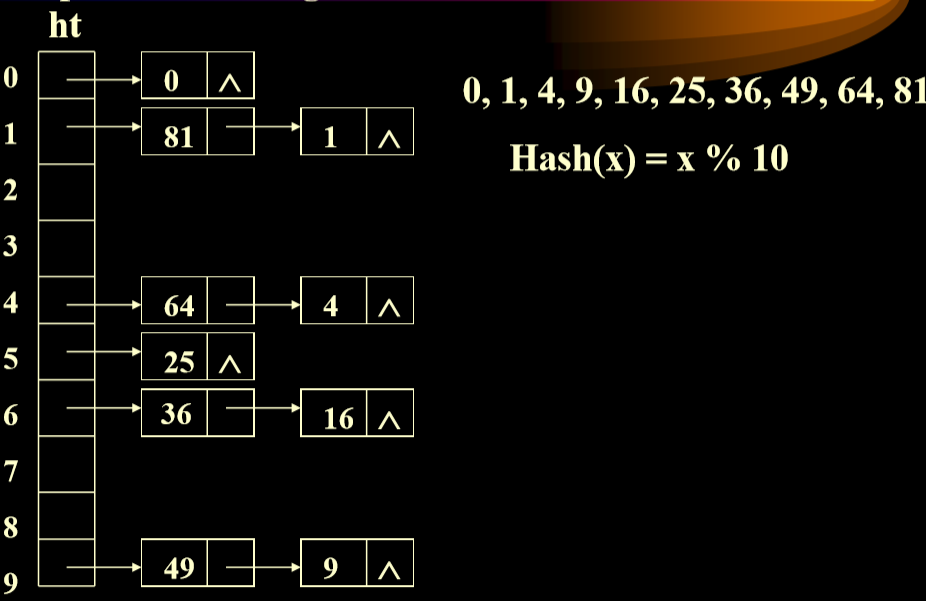
# 分离链接法 (Separate Chaining)
使用每个位置对应线性表解决这个问题,避免了出现向下进行顺延的情况。
# 代码实现
public class SeparateChainingHashTable { | |
public SeparateChainingHashTable( ) | |
public SeparateChainingHashTable( int size ) | |
public void insert( Hashable x ) | |
public void remove( Hashable x ) | |
public Hashable find( Hashable x ) | |
public void makeEmpty( ) | |
public static int hash( String key, int tableSize ) | |
private static final int DEFAULT_TABLE_SIZE = 101; | |
private LinkedList [] theLists; | |
private static int nextPrime( int n ) | |
private static boolean isPrime( int n ) | |
} | |
public interface Hashable{ | |
int hash( int tableSize ); | |
} | |
public class Employee implements Hashable { | |
public int hash( int tableSize ) { | |
return SeparateChainingHashTable.hash( name, tableSize ); | |
} | |
public boolean equals( object rhs ) { | |
return name.equals( ( Employee) rhs ).name ); | |
} | |
private String name; | |
private double salary; | |
private int seniority; | |
} | |
public SeparateChainingHashTable() { | |
this( DEFAULT_TABLE_SIZE ); | |
} | |
public SeparateChainingHashTable(int size) { | |
theLists = new LinkedList[ nextPrime( size ) ]; | |
for( int i = 0; i < theLists.length; i++ ) theLists[ i ] = new LinkedList( ); | |
} | |
public void makeEmpty( ) { | |
for( int i = 0; i < theLists.length; i++ ) | |
theLists[ i ].makeEmpty( ); | |
} | |
public void remove( Hashable x ){ | |
theLists[ x.hash( theLists.length ) ].remove( x ); | |
} | |
public Hashable find( Hashable x ) { | |
return ( Hashable ) theLists[ x.hash( theLists.length ) ]. Find( x ). Retrieve( ); | |
} | |
public void insert( Hashable x ) { | |
LinkedList whichList = theLists[ x.hash( theLists.length ) ]; | |
LinkedListItr itr = whichList.find( x ); | |
if( itr.isPastEnd( ) ) | |
whichList.insert( x, whichList.zeroth( ) ); | |
} |